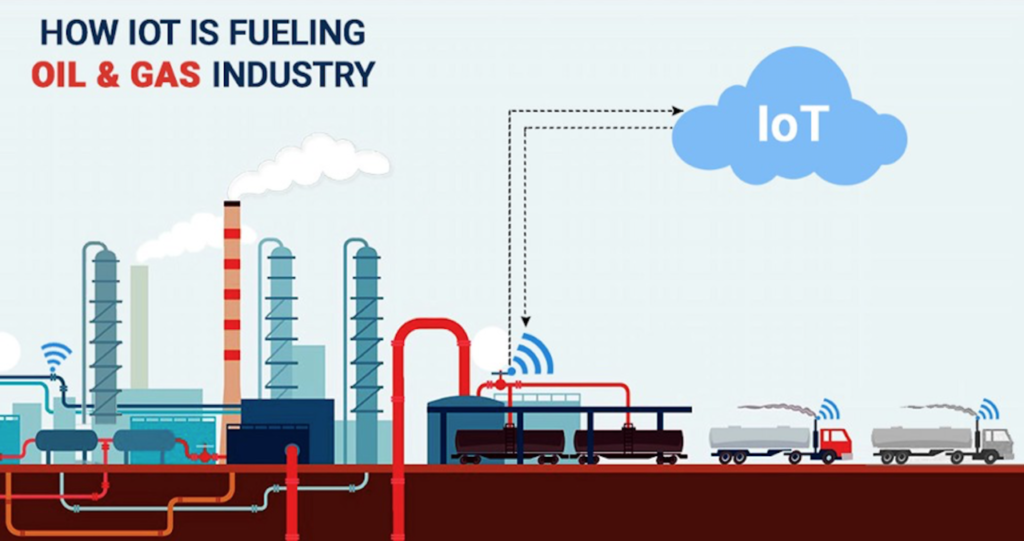
The Internet of Things (IoT) is used in the oil and gas industry to collect, transfer, and analyze raw data in real time to get a clear picture of processes at the facilities, improve operational efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and drive profitability. IoT solutions cover all key industry segments:
- Upstream operators use it to enhance drilling and extraction management and reduce non-productive time.
- Midstream operators improve fleet management as well as pipeline and storage maintenance.
- Downstream businesses leverage IoT for optimized oil and gas processing and distribution.
What is IoT?
IoT in the oil & gas industry is the network of physical objects connected to the Internet. Wearable devices, vehicles, equipment, buildings, and just about any other thing can be embedded with electronics, software, sensors, and network connectivity. Forward-thinking oil & gas organizations are focusing their IoT initiatives less on underlying sensors, devices, and smart things and more on developing bold approaches for managing data, leveraging to expand or redevelop IoT infrastructure, and developing new business models which is positively influencing the market outlook.
IoT helps in removing the physical barriers in Oil and Gas industry which would help the companies to reach broader target audiences and opening new business opportunities. Moreover, adopting a certain IoT innovation for oil and gas, increases the value of the company’s products for clients, boosts its status, and reduces business maintenance costs in the long term.
What does IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) Mean?
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) or Industrial Internet has been fueling digital transformations for nearly every global industry. The oil and gas sectors are no exception either. Also known as Industry 4.0, IIoT incorporates technologies such as big data and machine learning to harness massive volumes of sensor data.
The industrial internet of things (IIoT) is the use of smart sensors and actuators to enhance manufacturing and industrial processes. IIoT uses the power of smart machines and real-time analytics to take advantage of the data that “dumb machines” have produced in industrial settings for years. The driving philosophy behind IIoT is that smart machines are not only better than humans at capturing and analyzing data in real time, but they’re also better at communicating important information that can be used to drive business decisions faster and more accurately. Connected sensors and actuators enable companies to pick up on inefficiencies and problems sooner and save time and money, while supporting business intelligence efforts. In manufacturing, specifically, IIoT holds great potential for quality control, sustainable and green practices, supply chain traceability, and overall supply chain efficiency. In an industrial setting, IIoT is key to processes such as Predictive maintenance (PdM), enhanced field service, energy management and asset tracking.
Although IoT and IIoT have many technologies in common, including cloud platforms, sensors, connectivity, machine-to-machine communications and data analytics, they are used for different purposes. IoT applications connect devices across multiple verticals, including agriculture, healthcare, enterprise, consumer and utilities, as well as government and cities. IoT devices include smart appliances, fitness bands and other applications that generally don’t create emergency situations if something goes amiss. IIoT applications, on the other hand, connect machines and devices in such industries as oil and gas, utilities and manufacturing. System failures and downtime in IIoT deployments can result in high-risk situations, or even life-threatening ones. IIoT applications are also more concerned with improving efficiency and improving health or safety, versus the user-centric nature of IoT applications.
Usually in oil and gas domain, the terms IoT and IIoT are used interchangeably, although the technical meaning is different.
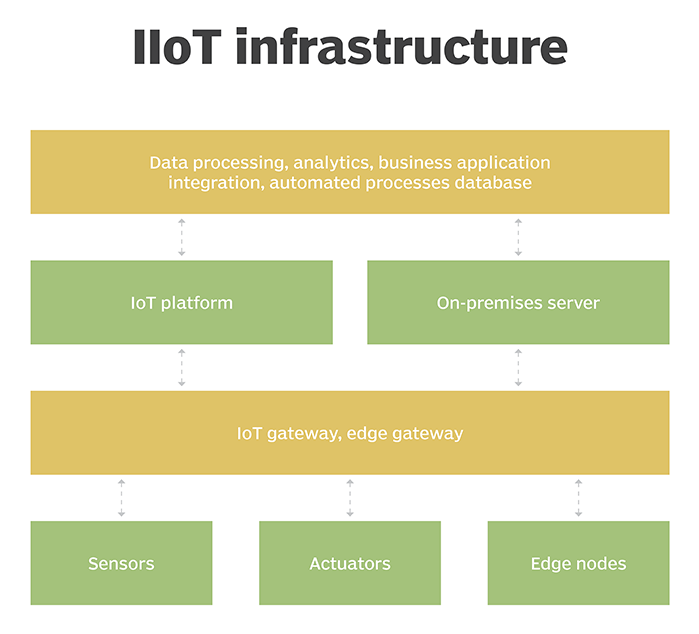
Recent Growth of IIoT in Oil and Gas Industry
The coronavirus pandemic declared as public health emergency worldwide by World Health Organization (WHO). Government across nations implemented lockdown and ban on travelling, shutdown of manufacturing industries, commercial activities this had severely disrupted the supply chain. However, during covid-19 outbreak IoT has aided the need for technological developments and new applications within different end-use verticals. Moreover, due to the spread of disease, the demand for integrating IIoT in oil & gas industries witnessed tremendous growth to enhance operational efficiency. Further, the spread of the pandemic resulted in a declining number of working staff. Hence, the demand for IIoT in oil and gas increased significantly to manage communication between physical objects of the industry and improve their efficiency.
According to UnivDatos Market Insights (UMI)’ research report “global IoT in oil and gas”, market expected to grow at a CAGR of around 22% during the forecast period (2021-2027). IIoT in oil and gas industry caters considerable demand across the globe and expected to have an influential market growth in the forecasted period. It is mainly owing to the factors such as Internet of Things (IoT), as a system integrator, helps in accumulating the complete oil and gas value chain within a single operating platform, addressing specific client-centric challenges, along with an improvement in overall performance.
In addition to this, the increasing threat of cyber-attacks and the decline in the availability of skilled labor in the oil and gas industry are other major factors fueling the market growth. Moreover, implementation of IIoT devices increases operational productivity, hence reduces operation risk, and improve intelligence and develop higher yield in labor and time-effective manner.
Based on Solution, the IIoT in oil and gas market is segmented into sensing, communication, cloud and edge computing and data management. The data management segment catered significant demand in IIoT in oil and gas market. Data management through IIoT enables users to refine massive data into essential information and helps the user track, monitor, and manage the devices efficiently, thereby augmenting the segment growth.
Based on industry stream, the IIoT in oil and gas market is classified into upstream, midstream, and downstream. The upstream segment holds the considerable market share in IIoT in oil and gas market. IIoT technologies in upstream sector simplify and make many processes more controllable within companies, as well as increasing the level of security of enterprises.
Based on application, the IIoT in oil and gas market is segmented into fleet and asset management, preventive maintenance, pipeline monitoring, security management and others. The fleet and asset segment hold the extensive market share in IIoT in oil and gas market. Asset management require for accurate day-to-day operational processes insights in oil and gas industry and machinery connected with IIoT devices predict when they require maintenance, so the repairs can be scheduled long before their breakdowns to prevent long downtimes and ensure the safety of the employees.
Benefits of IIoT in Oil and Gas Industry
- Real-time visibility. IIoT solutions provide real-time view into equipment performance and safety status, environmental conditions, and fleet operations, enabling oil and gas companies to continuously monitor their facilities and track ships or delivery trucks.
- Predictive maintenance. The data from IoT sensors installed at oil & gas facilities enables predictive analytics and root cause analysis (RCA). They help identify pre-failure conditions and perform maintenance in advance to avoid major downtimes and ensure smooth operation and smarter utilization of assets. This feature is especially helpful in maintaining remote offshore facilities, which often lack visibility and rely on manual check-ups. Employing IIoT helps optimize maintenance schedules there to avoid unnecessary visits of technicians while ensuring maximum equipment health.
- Hazard management. IIoT solutions monitor the presence of flammable gases and toxic vapors in the atmosphere and help prevent gas leakage or oil spills. Accident prevention capabilities of IIoT also make drilling and extraction operations safer and reduce injury rates by enabling advanced workplace safety monitoring and instant danger alerts.
- Improved bottom line. The IIoT-enabled benefits discussed above contribute to the cost efficiency of the industrial workflow. By optimizing the use of the facilities, equipment, resources, and workforce, the IIoT solutions provide oil and gas companies with the means to increase productivity and reduce expenditures, thus increasing the overall profits.
- Reduced environmental impact. Oil and gas industry is one of the largest contributors to climate change: via direct operations as well as the fuels that it produces, it accounts for over 40% of global greenhouse-gas emissions. To reduce their carbon footprint, upstream operators can reduce fugitive emissions and flaring with the help of IIoT-enabled leak detection and predictive maintenance, while downstream operators leverage IIoT to improve their energy efficiency.
- Regulatory compliance. Comprehensive data on facility operations provided by IIoT solutions paves the way for better compliance with industry standards and regulations.
The Added Value of IIoT in Oil and Gas Industry
IIoT technology is significantly making it possible to automate upstream oil drill operations, mid-stream pipeline operations, downstream refining operations, solar and wind farm operations. With the help of smart sensors and advanced gateways, companies could easily monitor the performance of a system in real-time, automatically adjust the industrial efficiency, and ensure better productivity at all stages.
Generating More Throughput
- Oil and Gas has a major impact on the global GDP: According to Oxford Economics, industry-wide adoption of IIoT could increase the global GDP by as much as 0.8 percent, or $816 billion in the next decade.
- The proliferation of IIoT in Oil and Gas greatly increases production throughput and efficiency across upstream, midstream and downstream operations, while also enhancing safety and reducing overhead costs.
- The use of sensors and monitoring systems, responsible for ingesting, managing, and processing data, lead to accelerated performance improvements.
- Using real-time data, Oil and Gas companies are increasingly able to gain end-to-end visibility into their operational processes, get a better understanding of their asset performance, and make informed decisions to improve field operations.
Equipment and Asset Management
- IIoT implementation makes it easier for companies to determine the remaining life of their assets and reconfigure them to avoid performance downtimes.
- Since sensors continually monitor each piece of functional equipment for anomalies and relay data to maintenance teams, organizations can respond faster to any imminent issues that might cause disruptions, ensuring continuous delivery without an impact to service.
Remote Performance Monitoring
- Given the extensive, multi-location footprint of Oil and Gas companies, IIoT meets the critical yet daunting need to evaluate asset performance remotely for efficiency, safety, and maintenance needs.
- Contrary to isolated, unconnected factories of the past, modern IIoT-led enterprises transform upstream operations by consolidating industrial data using sensors and gateways.
- These technologies monitor remote assets in real-time, communicate performance data across a common information layer, and help service teams better understand on-ground operations.
- Metrics, such as pressure and temperature, are tracked to monitor Oil and Gas equipment and are further compared to determine the maximum outputs and operational lags, if any.
- For example, companies can adapt their drilling strategies after comparing real-time down-hole drilling data with data from the production of nearby wells. According to Bain & Company, this level of visibility can help Oil and Gas companies improve production by 6% to 8%.
Predictive Maintenance (PdM)
- Oil and Gas companies use data insights to analyze the infrastructural health and predict problems and failures that might put operations under stress.
- Preventive maintenance helps enterprises spot anomalies in asset and equipment usage beforehand and initiate pre-emptive action to control damage.
- Organizations can develop bespoke counteractive strategies for every fault they detect and keep workflows stable resulting in improved efficiency, reliability and reduced operational costs.
Decreased Safety Risk
- Safety is perhaps the largest industry concern, both internally and externally.
- IIoT can lessen the risk taken by identifying potential issues before they become actual problems or safety hazards.
- Remote troubleshooting means more constant and efficient regulation of oil rigs.
- Fully leveraged IIoT integration also means less travel and potentially dangerous work for personnel.
Environmental Footprint
- From increased efficiency to lessened safety risk and reduced travel, IIoT adoption can significantly reduce the environmental impact of the Oil and Gas industry.
- Using less energy, avoiding oil spills and other accidents, and emitting less carbon is significant enough for Oil and Gas to pay attention to IIoT.
- IIoT also allows for clearer monitoring of energy and resource usage.
- The integration of connected devices in Oil and Gas will touch nearly every leg of the supply chain from operations to customer engagement. It’s an opportunity for rapid change in a legacy industry and a chance for Oil and Gas to compete in a commoditized world.
Conclusions
Over the past decade, the oil and gas industry has embraced IIoT technologies to optimize workflows across the stream, improve the safety and control of the work environment, and boost productivity. From minimizing manual maintenance, to automating error-prone complex tasks, to reducing environmental impact and preventing hazards – the capabilities of IIoT for oil and gas are vast. If you want to know how your organization can benefit from IIoT, our IIoT team is eager to study your specific needs and offer an optimal solution. Reach out to our specialists now!